ESP32
Light Sleep
Deep Sleep
Hibernation
Experimenting with ESP32 sleep modes
Tuesday, March 17, 2020
Setting Up The LED Control
Let’s start with the 3 LEDs, which are connected to pins GPIO27, GPIO25 and GPIO32 of the ESP32.
LED Configuration
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Definition of LED properties
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// RED YELLOW GREEN
// 0 1 2
const gpio_num_t LED_PINS[] = { GPIO_NUM_27, GPIO_NUM_25, GPIO_NUM_32 };
const uint8_t LED_NUMBER = 3;
// defines the index of the active LED
uint8_t ledIndex = 0;
We simply define a constant array that includes the pins of our LEDs, as well as a ledIndex variable that will allow us to browse this array to extract the pin of the LED we want to turn on from its index. The LED that will be lit by default is the red one, i.e. the one whose pin has the index 0 in the array.
Let’s then initialize the control pins of our LEDs as output pins, and turn on the active LED :
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialization
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
for (uint8_t i=0; i<LED_NUMBER; i++) {
pinMode(LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT);
}
digitalWrite(LED_PINS[ledIndex], HIGH);
}
LED Animation
Let’s now define a function to update the status of the LEDs that will be responsible for turning on the active one and turning off the others:
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Active LED lighting
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void updateLED() {
for (uint8_t i=0; i<LED_NUMBER; i++) {
digitalWrite(LED_PINS[i], i == ledIndex ? HIGH : LOW);
}
}
If we now wish to light each LED one by one, cyclically, for a brief moment repeating this procedure indefinitely, we need only define the main loop as follows:
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main control loop
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
updateLED();
++ledIndex %= LED_NUMBER;
// which is equivalent to:
// ledIndex = ledIndex + 1;
// ledIndex = ledIndex % LED_NUMBER;
}
Let’s observe what happens as we execute our code:
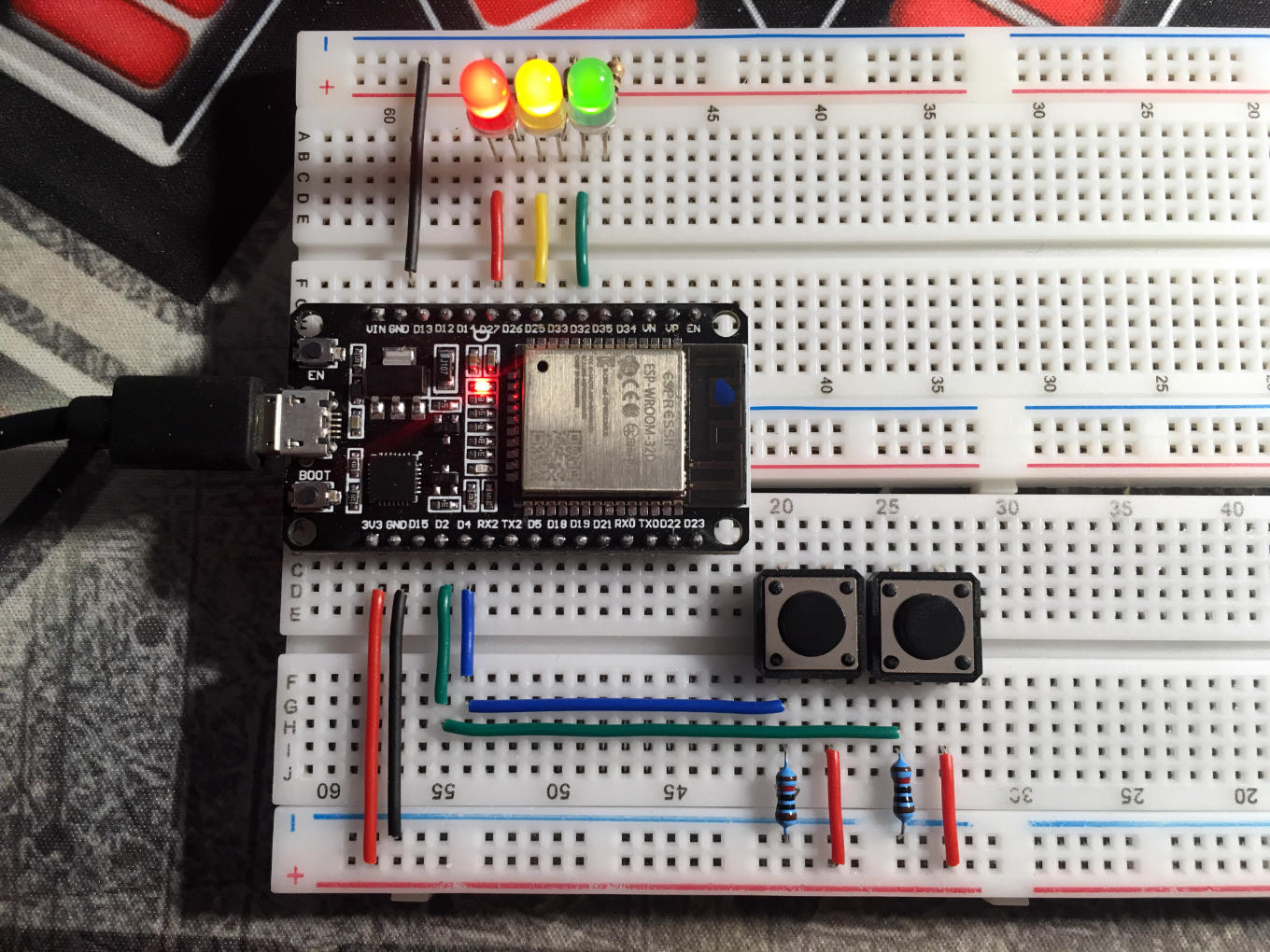
All LEDs light up at the same time…
But how come? We made sure to scan each LED one by one!
The reason is simple: the scanning is actually done by lighting one LED at a time, but the loop runs so fast that the retinal persistence gives us the impression that they are all lit at the same time, when in reality, they are not!
Delaying The Animation
To better observe the phenomenon, simply add a slight delay (say 200 ms) at the end of each cycle of the main loop:
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main control loop
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
updateLED();
++ledIndex %= LED_NUMBER;
delay(200);
}
And this time, it’s clear that the scan is proceeding normally:
The Resulting Code
To conclude this chapter, here is the complete code of our first experiment:
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Definition of LED properties
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// RED YELLOW GREEN
// 0 1 2
const gpio_num_t LED_PINS[] = { GPIO_NUM_27, GPIO_NUM_25, GPIO_NUM_32 };
const uint8_t LED_NUMBER = 3;
// defines the index of the active LED
uint8_t ledIndex = 0;
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialization
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
for (uint8_t i=0; i<LED_NUMBER; i++) {
pinMode(LED_PINS[i], OUTPUT);
}
digitalWrite(LED_PINS[ledIndex], HIGH);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Active LED lighting
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void updateLED() {
for (uint8_t i=0; i<LED_NUMBER; i++) {
digitalWrite(LED_PINS[i], i == ledIndex ? HIGH : LOW);
}
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Main control loop
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop() {
updateLED();
++ledIndex %= LED_NUMBER;
delay(200);
}